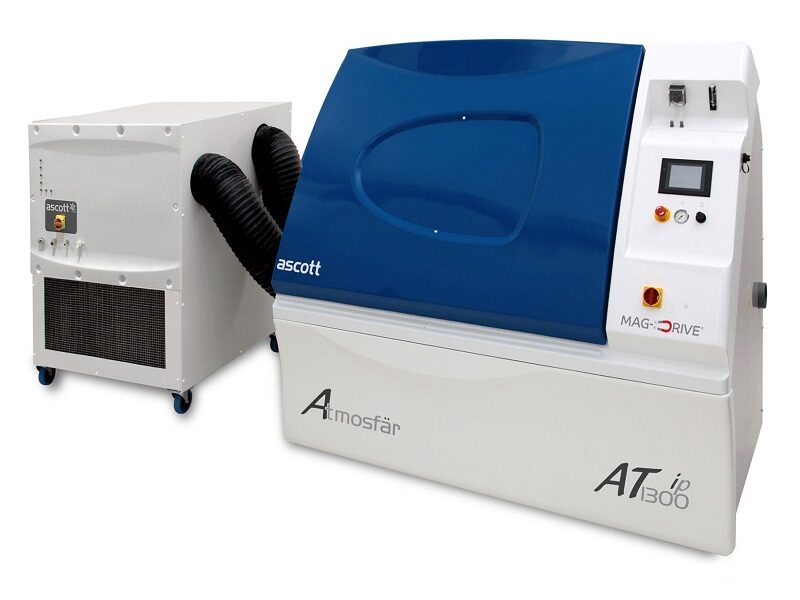
Salt Spray Testing.
Salt spray testing in accordance with ASTM B117 , ISO 9227 and ASTM G85 (modified salt spray) are accelerated corrosion tests, used in the evaluation of coatings and surface treatments. Salt spray testing evaluates a coating or surface treatments ability to resist corrosion.
The salt spray tests are particularly useful for detecting discontinuities, such as pores and other defects, in certain metallic, organic, anodic oxide and conversion coatings. Giving an indication to a coating or finish’s ability to resist corrosion during its life in service. With a total of over 12,000 litres of test chamber availability, Aerofin are able to offer rapid response for urgent testing requirements.
Salt Spray on Coated Samples
The salt spray tests are particularly useful for detecting discontinuities, such as pores and other defects, in certain metallic, organic, anodic oxide and conversion coatings. Giving an indication to a coating or finish’s ability to resist corrosion during its life in service.
Salt spray testing can be useful tool for evaluating finishes such as paint, powder coatings & e-coatings. Where prior to exposure defects can be introduced in the form of scribe lines & evaluated for undesirable defects such as delamination & filiform corrosion, methods include:
- ISO 4628-8 Assessment of degree of delamination and corrosion around a scribe or other artificial defect.
- ISO 4628-10 Assessment of degree of filiform corrosion.
Evaluations remote from a scribe mark can include:
- ISO 4628-2 Assessment of degree of blistering.
- ISO 4628-3 Assessment of degree of rusting.
- ISO 4628-4 Assessment of degree of cracking.
- ISO 4628-5 Assessment of degree of flaking.
- ISO 4628-6 Assessment of degree of chalking by tape method.

Salt Spray Conditioning
Salt spray testing can be used as a preliminary exposure to other testing. Where the salt spray aspect is used to artificially age the coating or finish & the post exposure test evaluates performance capabilities to assess appropriate application for its intended purpose. Common post exposure testing include:
- ISO 1518-1 / ISO 1518-2 Determination of scratch resistance.
- ISO 15184 Determination of film hardness by pencil test.
- ISO 6272 / ASTM D2794 rapid deformation by impact.
- ISO 2409 Paints and varnishes — Cross-cut test.

Common Types of Salt Exposure
The most common type of salt spray testing is Neutral fog in accordance with ASTM B117 & ISO 9227. Where specimens are exposed to a steady stream of neutral fog, atomised inside a sealed inert chamber. The duration of exposure is dictated by relevant standard/specification or the customers bespoke requirements. Quantitative & qualitative evaluation can be made at regular interval during testing & on completion of the entire exposure period. Common evaluation methods of inorganic coatings on metallic substrates include:
- ASTM G46 examination & evaluation of pitting corrosion.
- ISO 10289 method for corrosion testing of metallic and other inorganic coatings on metallic substrates – rating of test specimens and manufactured articles subjected to corrosion tests.
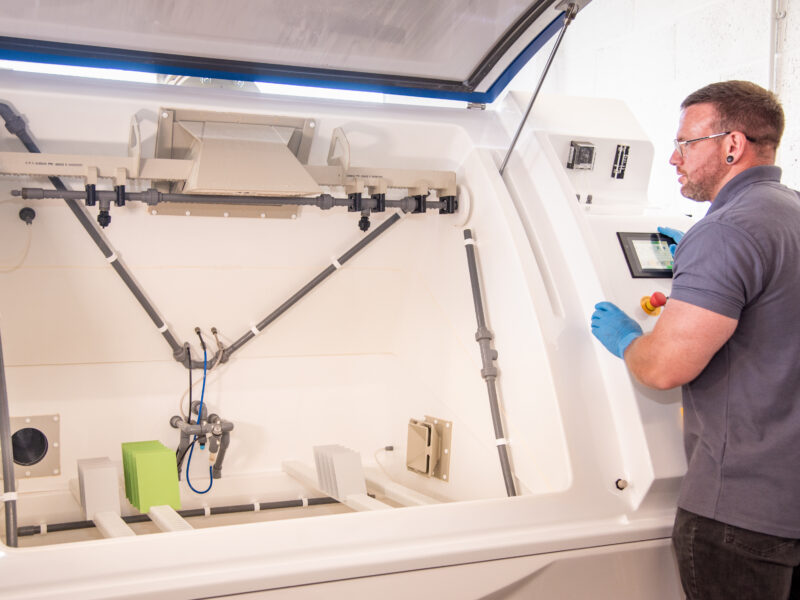

Salt Spray Variations
Salt spray testing can be performed at various salt concentrations, with 5% being the most commonly used. Variations include the addition of other corrosive chemicals. The addition of such chemicals as Acetic acid & copper chloride increase the rate of corrosion, producing results in a shorter period of time. Testing specifications include:
- ISO 9227 Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres – salt spray tests.
- ASTM G85 standard practice for modified salt spray (fog) testing.
- ASTM B 368 standard test method for copper accelerated acetic acid salt spray (fog) testing.
For information on salt spray chambers visit; www.ascott-analytical.com



